As demand for organic food grows, so does the demand for organic seed and suited cultivars.
To reach 100% use of organic seed adapted cultivars we need to overcome several challenges:
 technical difficulties in organic seed production
technical difficulties in organic seed production inconsistent implementation of EU organic regulation
inconsistent implementation of EU organic regulation lack of transparency regarding the availability and demand of organic seed
lack of transparency regarding the availability and demand of organic seed insufficient organic breeding programs
insufficient organic breeding programs
The objectives and aims of LIVESEED are to improve transparency and competitiveness of the organic seed and breeding sector and encourage greater use of organic seed. LIVESEED strives to:
 Foster harmonised implementation of the EU organic regulation on organic seed
Foster harmonised implementation of the EU organic regulation on organic seed Strengthen organic seed databases in the whole EU
Strengthen organic seed databases in the whole EU Investigate socio-economic aspects related to production and use of organic seed
Investigate socio-economic aspects related to production and use of organic seed Improve availability and quality of organic seed
Improve availability and quality of organic seed Develop guidelines for organic cultivar testing and registration
Develop guidelines for organic cultivar testing and registration Develop innovative breeding approaches suited to organic farming
Develop innovative breeding approaches suited to organic farming Widen the choice of organic cultivars meeting the demand of farmers, processors, retailers and consumers
Widen the choice of organic cultivars meeting the demand of farmers, processors, retailers and consumers Research activities of LIVESEED will cover five main crop categories (legumes, vegetables, fruit trees, cereals and fodder crops) considering different farming systems and pedoclimatic zones across Europe
Research activities of LIVESEED will cover five main crop categories (legumes, vegetables, fruit trees, cereals and fodder crops) considering different farming systems and pedoclimatic zones across Europe
“I hope that at the end we can offer recommendations to the national authorities and the EU on how to harmonise the implementation of the EU regulation on organic seed”
Monika Messmer, FiBL-CH scientific coordinator
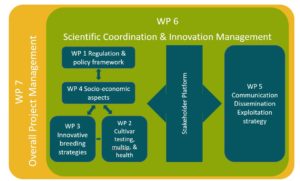
Structure of LIVESEED Work Packages (WP)
Read more details about each WP in this document.
Specific objectives
- Provide a level playing field regarding the use of organic seed across Europe (WP1) by (i) analysing the determinants of the current production and use of organic seed, (ii) identifying breeding gaps of crops and sub-crops where suited cultivars are missing, (iii) increasing transparency of the EU organic seed market, (iv) improving the implementation of legislative requirements in close collaboration with national authorities in EU Member States, and (v) developing missing national databases together with an EU-wide router database tool for seed suppliers.
- Increase the volume and quality of organic seeds derived from cultivars suited for organic farming (WP2) by (i) developing and improving efficiency of cultivar testing models under organic farming for the identification of suited cultivars, (ii) developing adjusted protocols for DUS and VCU examination suited for the official variety registration of open pollinated varieties and new descriptors for marketing of heterogeneous population, (iii) sharing of knowledge and training on smart practices for organic seed multiplication across countries, and (iv) investigating novel seed health strategies and technologies focusing on the vitality of organic seed.\
- Accelerate the breeding process and adoption of new cultivars (WP3) by (i) developing novel and holistic breeding concepts and approaches, from trait based to system based breeding, (ii) delivering new breeding tools based on better scientific understanding of the biological basis of crop resilience and product quality, plant-plant, and plant-microbe interactions, (iii) strengthening small breeding initiatives and stimulating collaboration among actors to close breeding gaps for the five main crop categories: legumes, cereals, vegetables, fruit trees and fodder crops, and (iv) identifying key factors for successful breeding initiatives.
- Improve the competitiveness of the organic seed sector (WP4) by (i) identifying gaps and bottlenecks in the market development of organic seeds and breeding through stakeholder consultations, (ii) analysing the organic seed market supply chain, (iii) developing business and governance models including all actors of the supply chain (breeders, seed producers, farmers, processors, retailers and consumers, (iv) performing case studies on the socio-economic impact of upscaling organic seed and (iv) studying consumer attitudes to the use of new breeding techniques.
- Enhance greater uptake of organic seed (WP5) by (i) knowledge sharing and disseminating of LIVESEED results (i) building the capacity of breeders, seed producers, farmers, retailers, researchers, and other actors of the food value chain through training and networking, and (iii) raising awareness of policy-makers regarding the importance of using organically bred seeds in organic farming.
- Foster seed and breeding related innovation in the organic sector (WP6) by (i) coordinating and ensuring scientific exchange between WPs and other related Seed Projects, (ii) fostering strong collaboration between academic and non-academic actors along the food value chain including competent authorities and policy makers and (iii) synthesising project results and developing joint-up recommendations .
 Liveseed
Liveseed Liveseed
Liveseed